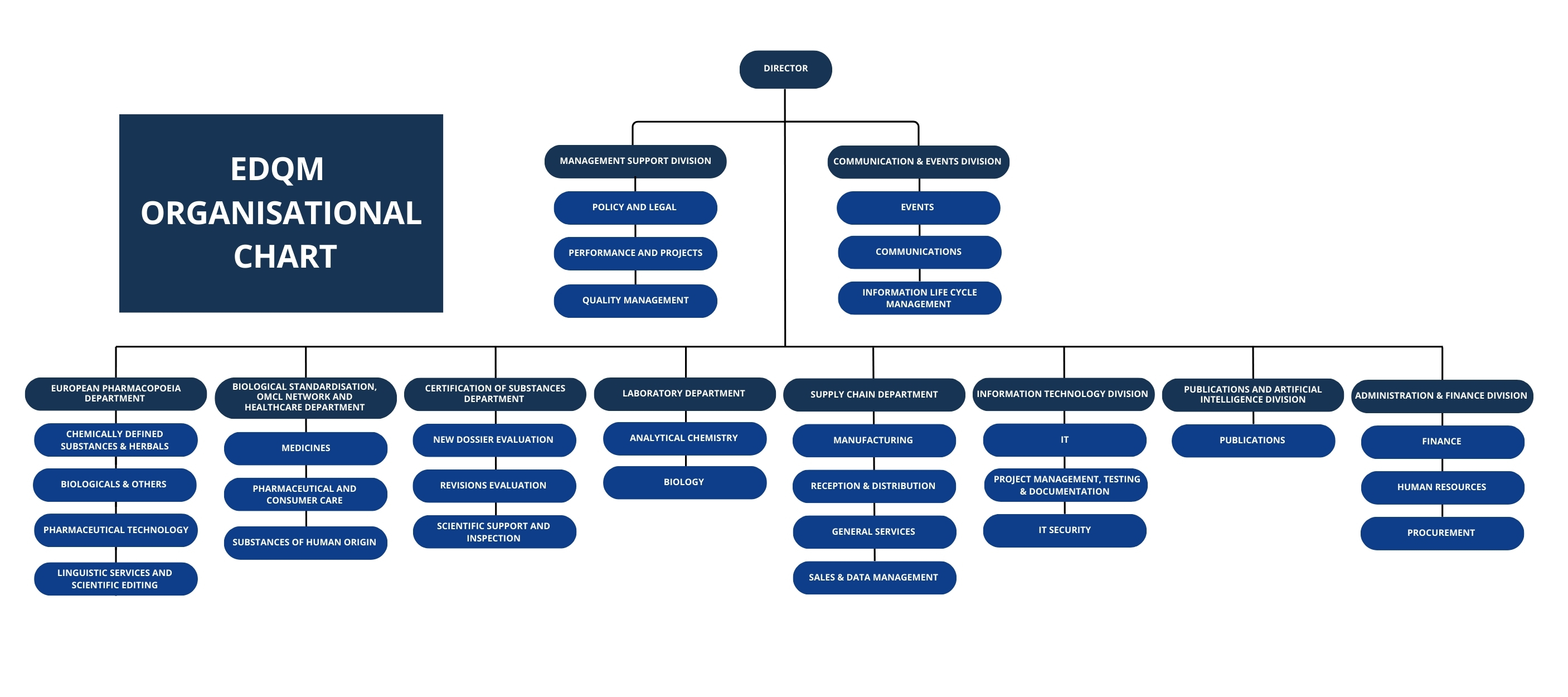
Structure
What is the EDQM?
The European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare (EDQM) is a directorate of the Council of Europe.
It dates back to the 1960s, when the Council of Europe’s vision of harmonising certain standards in the health sector, and thereby facilitating mutual aid and co-operation between European countries, led to the adoption of the Convention on the Elaboration of a European Pharmacopoeia (or the Ph. Eur. Convention for short) in 1964.
A technical secretariat was initially set up as foreseen in the convention, and over the years it has grown in both size and ambition, progressively taking on more and greater missions, with successive name changes reflecting its evolving status. Today, the EDQM is recognised as a leading entity in public health protection. Its broad network of dedicated stakeholders showcases the collective commitment to upholding the highest standards in public healthcare.
The EDQM is active in four areas of work:
- medicines;
- substances of human origin;
- pharmaceutical care;
- consumer health.
It employs over 400 highly qualified staff and is composed of ten administrative entities.
European Pharmacopoeia Department
The European Pharmacopoeia Department (EPD) is responsible for the Secretariat of the European Pharmacopoeia Commission (EPC) and for preparing the texts of the European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) with the relevant groups of experts.
The purpose of the Ph. Eur. is to ensure that medicines, for human or veterinary use, are safe and of good quality. It currently compiles over 3 000 legally binding, official quality standards (called monographs) for medicines and their components. Member states having ratified the Ph. Eur. Convention must ensure that these standards are respected when authorising a medicine for use by patients. They are also applied in many other countries worldwide.
To elaborate the Ph. Eur., the EPD works with a network of almost 900 experts with an extensive scientific background in different disciplines and from all over Europe and beyond. They represent national authorities (e.g. pharmacopoeial authorities, official medicines control laboratories, licensing authorities and inspectorates), the private sector (pharmaceutical and chemical industries), academia or research organisations. The Ph. Eur. work programme is allocated to over 60 working groups and working parties which hold regular meetings during the year.
The EPC, the governing body of the Ph. Eur., holds three sessions per year to formally adopt not only the Ph. Eur. texts, but also its work programme and to appoint Ph. Eur. experts.
The EPD also co-ordinates the Biological Standardisation Programme (BSP) whose purpose is to establish reference materials and standardise analytical procedures for the quality control of biologicals. The BSP also participates in the development and validation of alternative methods for the replacement of animals in laboratory experiments based on the 3R principles (replacement, reduction and refinement).
Certification of Substances Department
The Certification of Substances Department (DCEP) is responsible for implementing the procedure for the certification of suitability to the monographs of the European Pharmacopoeia (or the CEP procedure, for short). This is a centralised procedure used to demonstrate that the quality of a substance for pharmaceutical use is suitably controlled by the corresponding Ph. Eur. monograph and complies with regulatory requirements.
Certificates of Suitability (CEPs) are used by the pharmaceutical industry in their marketing authorisation applications for medicines and are recognised by national licensing authorities in Europe and beyond. Having one centralised procedure saves time and resources for regulatory authorities and industry alike.
As part of the CEP procedure, the DCEP is also responsible for conducting inspections of manufacturers of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Inspections ensure that substances are produced in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practices and that the information provided in CEP application dossiers is accurate. This includes liaising with the relevant authorities. If deficiencies are detected, inspectors follow up corrective actions.
The DCEP works with a network of nearly 150 experts (quality assessors and inspectors) nominated by national competent authorities.
Supply Chain Department
The Supply Chain Department (SCD) is responsible for the Supply & Operation Planning (S&OP), scientific procurement of raw materials, manufacturing and logistics operations (warehousing and dispatch), processing users’ orders and dealing with related queries.
The SCD also maintains the catalogue of Ph. Eur. reference standards, World Health Organization (WHO) International Standards for Antibiotics and WHO International Chemical Reference Standards. This encompasses the classification of all substances used in their preparation and the drafting of the necessary safety data sheets.
Lastly, the SCD is responsible for the EDQM’s general services (building facilities, furniture, mail service, etc.) and its environment, health and safety management systems.
Laboratory Department
The Laboratory Department (DLab) supports the work of the Ph. Eur. by conducting analytical studies to establish reference standards, as well as by assisting the Ph. Eur. expert groups in the analytical verification of new or revised Ph. Eur. monographs or general chapters in which these reference standards are cited.
The official Ph. Eur. reference standards are essential for the application of the quality-control tests described in the Ph. Eur. monographs. They are needed to identify the pharmaceutical substance or product tested, determine its content or potency and control impurities that may originate from its manufacturing process.
The DLab is also involved in establishing WHO International Standards for Antibiotics and Chemical Reference Standards.
The scientific expertise and the technical equipment of the EDQM Laboratory, attested by ISO 17025:2017 accreditation, ensure that official Ph. Eur. reference standards can be used by all manufacturers and independent control laboratories as a reliable means of controlling the quality of medicines and their ingredients.
Intergovernmental Committees and Networks Department
The remit of the Intergovernmental Committees and Networks Department (ICND) covers a broad range of areas.
The ICND provides the secretariat for several steering committees in charge of the implementation of work programmes aimed at protecting public health in several different fields. This includes:
- providing legal tools and guidance to national authorities in the fight against falsified medical products;
- providing guidance to professionals in the pharmaceutical care field to promote knowledge, skills and values in care and practices involving medicines;
- setting specific quality standards for the correct preparation of unlicensed medicines suitable for children to support healthcare professionals;
- setting ethical, safety and quality standards for substances of human origin used in medical therapies (e.g. blood, organs, tissues and cells);
- developing standards to improve the protection of consumers in Europe in the areas of food contact materials and cosmetics.
The ICND also co-ordinates the activities of two important networks of national control laboratories, the OMCL Network and the OCCL Network.
The first is a network of official medicines control laboratories (OMCLs). Its objective is to ensure the consistent quality of medicines for human and veterinary use and to foster mutual recognition of the results of quality-control testing by OMCLs to make best use of limited resources. It co-ordinates independent market surveillance programmes at European level to monitor the quality of medicines throughout their entire lifecycle.
The second is a network of official cosmetics control laboratories (OCCLs). They test the quality and safety of cosmetics at national level and, by sharing their knowledge and expertise, enhance their capacity to protect consumers. The initiatives co-ordinated by the OCCL Network provide dedicated support to ensuring consumer safety across the EU, as well as compliance with the EU single market provisions.
The ICND works with around 1 200 experts nominated by member states.
IT Division
The IT Division (ITD) is responsible for providing information technology equipment, services and security, including the management of all EDQM IT projects.
The ITD handles the development and maintenance of public and restricted-access European databases, such as the Knowledge database, the CRS catalogue and the CEP and Melclass databases. It also supports the implementation and maintenance of EDQM-wide IT applications.
Publications and AI Division
The Publications and AI Division (PAID) co-ordinates the EDQM’s publication projects in collaboration with specialised departments of the EDQM, which are responsible for their elaboration. They include the European Pharmacopoeia itself and numerous technical guides, such as those on blood transfusion and organ, tissue and cell transplantation. In co-operation with the Council of Europe Directorate of Information Technology, the PAID explores the potential applications of artificial intelligence within the EDQM.
Communications and Events Division
The Communications and Events Division (CED) is responsible for the EDQM’s communications, public relations, and information lifecycle management activities.
Communication projects are run in collaboration with the respective specialised departments. The aim is to develop and maintain communication with the EDQM’s stakeholders and media in Europe and beyond via the EDQM website, social media channels, print and electronic publications, and promotional campaigns.
The CED also organises a wide range of events, from conferences, training sessions and seminars to visits of the EDQM premises and numerous online events such as webinars. It also represents the EDQM at international trade exhibitions and other events.
The Information Lifecycle Management section, within the CED, maintains and develops the Electronic Document & Record Management System (EDRMS) and handles paper archives and digitisation projects. It also manages the EDQM Library, which makes a wide variety of specialised publications and periodicals available to EDQM staff. Finally, the CED operates the EDQM HelpDesk, which fields questions from EDQM users year-round.
Administration and Finance Division
The Administration and Finance Division (DAF) is responsible for the administrative and financial management of the EDQM, which includes overseeing the budget, validating financial transactions and managing the recruitment and development of staff and seconded personnel.
The DAF prepares and monitors the EDQM budgets, validates all financial requests and processes requests for payment. It also accounts for fixed assets and stocks and calculates the costs of EDQM activities.
The DAF is also responsible for processing users’ orders for EDQM products, issuing invoices and dealing with related queries.
In terms of human resources, the DAF organises recruitment exercises and the training programme and oversees the assessment process for the EDQM staff.
These activities are carried out in close collaboration with the Council of Europe’s Programme and Budget Directorate and the Directorate General of Administration.
Management Support Division
The Management Support Division (MSD) is responsible for enhancing the strategic and operational frameworks within the EDQM. The MSD co-ordinates the development and implementation of the EDQM’s mid- and long-term strategies, tracks and reports on the progress of strategic programmes and projects and supports the EDQM management team through data gathering and performance analysis.
The MSD also provides policy advice, notably leading and co-ordinating horizon-scanning on emerging topics in regulations, policy and technology that could impact the EDQM’s activities. In collaboration with the Council of Europe’s Directorate of Legal Advice and Public International Law, it ensures the provision of legal advice to minimise the EDQM’s exposure to legal risks.
The Quality and Risk Management Section (QRMS), within the MSD, co-ordinates the development and maintenance of the EDQM’s quality and risk management systems, which aim to continually improve EDQM products and services and ensure business continuity. This includes maintaining an up-to-date EDQM Risk Register.
As part of the EDQM’s efforts to drive continuous improvement, the QRMS co-ordinates the implementation of ISO 9001 principles, ISO 17025 accreditation activities and performs internal audits.
Moreover, the QRMS is responsible for releasing the reference standards produced at the EDQM.